Helicopter imaging
mission specific
Instrument Overview
The Mars 2020 rover carries a helicopter as a technology demonstration. The helicopter will fly up to 5 times over a ~30 sol period early in the mission. The helicopter carries two cameras, one for navigation and one for capturing aerial views for science evaluation. The images are stored onboard during flight, and then are transmitted to the rover afterward for relay to Earth.
Characteristics of the two cameras are shown in the table below.
| Helicopter Cameras Operational Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Navigation camera | RTE (Return to Earth) camera |
| Resolution (S x L) | 640 x 480 | 4224 x 3120 |
| Bit Depth | 8 | 8 |
| Field of View (FOV) | 133 x 100 deg | 101 x 82 deg |
| Angular Resolution | 3.6 mrad/pix | 0.26 mrad/pix |
| Number of Spectral Filters | 0 (monochrome detector) | 0 (color detector) |
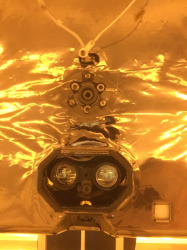
Helicopter cameras photo, bottom view: RTE is at the lower corner in the indentation. Navigation Camera is the "nose" in the oval cutout.
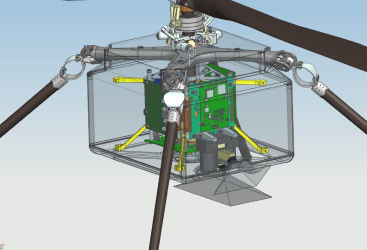
Helicopter cameras location and viewing frustrums. Navigation Camera looking straight down, RTE angled.
Helicopter Navigation Camera
The helicopter navigation camera is a 640 x 480 pixel, 8-bit, grayscale camera. It points straight down from the belly of the helicopter (see figures above). It is used by the onboard navigation software to determine helicopter position and attitude, and to help navigate to the desired destination. Selected images may be returned to Earth for analysis.
Helicopter Return to Earth Camera
The helicopter “Return to Earth” camera is a 4224 x 3120 pixel, 8-bit, color camera. It is mounted on the side of the helicopter and faces down at a 45 degree angle so it can see both nadir and horizon (see figures above).